The Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a comprehensive analysis and guide to setting up a float glass manufacturing facility. Float glass is a critical material used across various industries, such as construction, automotive, and electronics. The demand for high-quality glass has surged in recent years, making it an attractive area for new business ventures. This report outlines the essential aspects of a float glass manufacturing plant, including its planning, setup, process, equipment, raw materials, and economic feasibility. For businesses or entrepreneurs interested in starting a glass manufacturing venture, understanding the technical and financial requirements is essential for success.
1. Understanding Float Glass
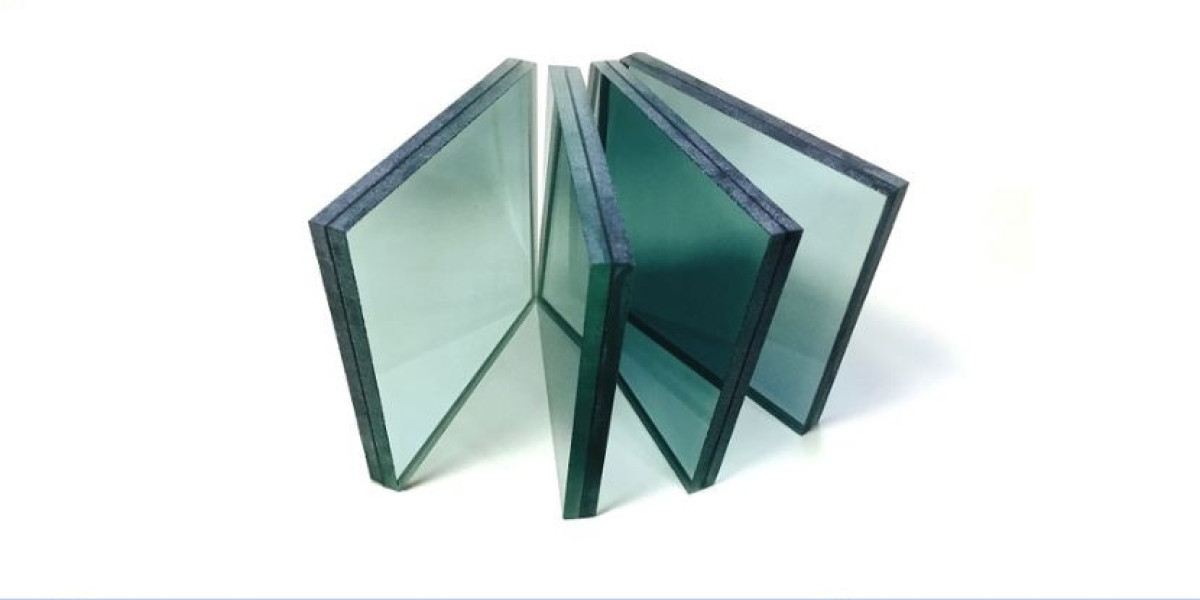
Before diving into the specifics of a Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report, it's important to understand what float glass is and why it is so valuable in a wide array of industries. Float glass is a type of flat glass that is produced through a unique process known as the "float glass process." This method involves floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin, which gives the glass a perfectly smooth and uniform surface.
Float glass has a wide range of uses, including for windows, mirrors, and architectural glazing, as well as in the production of automotive glass. Due to its superior quality, uniform thickness, and optical clarity, float glass is considered ideal for applications where aesthetics and durability are crucial. The manufacturing process, therefore, needs to be precise and controlled to ensure high-quality output.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
2. The Float Glass Manufacturing Process
A Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report would not be complete without discussing the manufacturing process itself. The production of float glass is an intricate process involving several critical stages. These steps need to be carefully optimized to ensure high-quality glass output. The key stages are as follows:
Raw Material Preparation
The first step in the float glass manufacturing process involves preparing raw materials. The primary raw materials include:
- Silica Sand: The main component in the production of glass.
- Soda Ash: Used to lower the melting point of silica.
- Limestone: Added to improve the durability of the glass.
- Alumina and Magnesia: Added for the glass to be resistant to scratching.
- Other Additives: For coloring and coating the glass.
These materials are mixed in the right proportions and transported to the melting furnace.
Melting Furnace
The raw materials are fed into a high-temperature furnace where they are melted at temperatures exceeding 1,500°C. The molten glass is then formed into a continuous ribbon.
Float Process
The molten glass is directed into a large molten tin bath. The glass naturally floats on the tin due to the difference in densities between the two materials. This process allows for the creation of large, flat, and uniform sheets of glass. The thickness of the glass can be controlled by adjusting the rate at which the molten glass enters the tin bath and the temperature.
Annealing Process
After the glass has been formed, it moves through an annealing lehr, a controlled cooling system that gradually reduces the temperature of the glass. This step is crucial for relieving internal stresses in the glass that could lead to breakage or warping. The cooling process also ensures that the glass does not develop surface defects.
Cutting and Finishing
Once the glass has cooled, it is cut into sheets of various sizes based on the customer’s specifications. Depending on the end use, additional processes such as polishing, coating, tempering, and laminating may be applied to enhance the glass's properties and appearance.
3. Key Components of a Float Glass Manufacturing Plant
In a Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report, it is important to cover the technical infrastructure that is required for the plant's operation. The core components include:
Land and Infrastructure
The land chosen for the float glass manufacturing plant should be large enough to accommodate the plant and provide space for future expansion. Additionally, the infrastructure must include access to water, electricity, and transportation networks for raw materials and finished products.
Machinery and Equipment
The float glass manufacturing process requires specialized machinery to handle different stages of production:
- Melting Furnace: For melting raw materials into molten glass.
- Tin Bath: A bath of molten tin where the glass is floated to form a smooth surface.
- Annealing Lehr: A cooling system for controlled cooling of glass sheets.
- Cutting and Processing Machinery: For cutting, polishing, and coating the glass.
All of these machines must be equipped with state-of-the-art control systems to ensure optimal production and high-quality output.
Raw Material Storage and Handling
Proper storage systems must be in place to manage the raw materials. The materials should be stored in separate, clearly labeled sections to avoid contamination. Efficient handling systems, including conveyors and forklifts, are necessary to transport materials throughout the plant.
Laboratory and Testing Equipment
Quality control is vital in the float glass manufacturing process. A laboratory equipped with advanced testing tools is necessary to assess the properties of the glass, including its thickness, clarity, and strength. These tests ensure that the glass meets the required standards for different applications.
4. Economic Feasibility and Investment
The Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report must include a detailed financial analysis to determine the economic viability of the venture. Key factors to consider in this analysis include:
Capital Investment
Setting up a float glass manufacturing plant requires significant capital investment. This includes costs for land, construction, machinery, and equipment. Additionally, investments will be required for the procurement of raw materials, labor, and utilities.
The cost of setting up such a facility can run into millions of dollars, making it essential to conduct a detailed cost-benefit analysis and secure financing from banks or investors.
Operational Costs
Operating a float glass manufacturing plant incurs various costs, including:
- Raw Material Costs: The cost of silica sand, soda ash, limestone, and other raw materials.
- Labor Costs: Wages for skilled and unskilled laborers, including workers for the furnace, annealing, and cutting processes.
- Energy Costs: The production of float glass is highly energy-intensive, particularly the melting and floating processes.
- Maintenance and Overheads: Regular maintenance of machinery and equipment is required to ensure smooth operations, and administrative costs must be considered as well.
Revenue Generation
The revenue for a float glass manufacturing plant primarily comes from the sale of glass sheets. To maximize profitability, the plant can offer various types of glass, such as tempered, laminated, or coated glass. Diversifying the product line to cater to the demands of different industries can increase revenue potential.
Market Demand and Pricing
The demand for float glass is influenced by multiple factors, including construction activities, advancements in the automotive sector, and technological innovations in the electronics industry. Understanding market trends and setting competitive pricing strategies is essential to maintain profitability.
5. Location and Market Analysis
When developing a Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report, the location of the plant is a key consideration. Factors that should be taken into account include:
- Proximity to Raw Material Sources: Locating the plant near suppliers of raw materials such as silica sand can reduce transportation costs.
- Transportation and Logistics: The plant should be located near highways, railways, and ports for easy distribution of both raw materials and finished products.
- Labor Availability: Access to a skilled workforce is essential for operating the plant efficiently. Additionally, the cost of labor in the region should be considered.
- Regulatory Environment: Local laws and regulations regarding industrial operations, safety, and environmental impact should be taken into account when choosing a location.
6. Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
A Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report must also address the environmental impact of the plant and compliance with regulations. The manufacturing of float glass is energy-intensive and generates significant emissions. Therefore, the project must incorporate strategies for minimizing environmental damage. This includes:
- Energy Efficiency: Installing energy-efficient furnaces and using alternative energy sources like solar or wind power can reduce the plant’s carbon footprint.
- Emission Control: The plant should have effective filtration and scrubbing systems to control air emissions.
- Waste Management: Proper waste management systems should be in place to handle both solid and liquid waste from the production process.
7. Risk Assessment
No Float Glass Manufacturing Plant Project Report is complete without a thorough risk assessment. Risks that need to be considered include:
- Raw Material Price Fluctuations: The price of key raw materials like silica sand and soda ash can fluctuate, affecting production costs.
- Energy Price Volatility: Energy costs can impact the profitability of the plant due to the high energy demands of glass manufacturing.
- Market Competition: The float glass industry is highly competitive, and the plant will need to differentiate itself through quality, customer service, or pricing strategies.
- Environmental Regulations: Stricter environmental regulations could result in higher compliance costs or even plant shutdowns if the plant fails to meet required standards.
By understanding and addressing these risks, the plant can be better positioned for long-term success in the competitive float glass market.
Media Contact
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Peter Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au